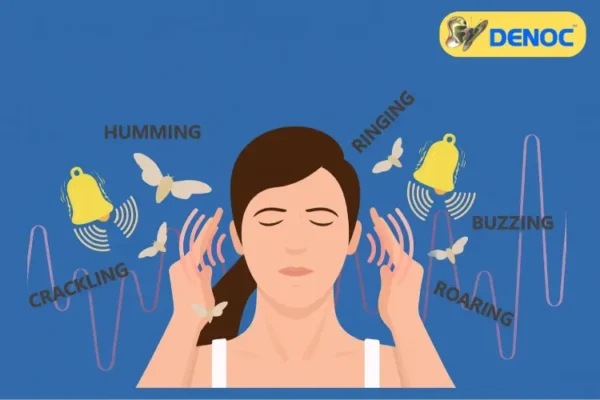
🔔 What is Tinnitus?

Tinnitus is the perception of sound — like ringing, hissing, whistling, or clicking — in one or both ears when no external sound is present. It can be either:
- Subjective: Heard only by the affected person
- Objective: Rare form where others can also hear it
❓ Is Tinnitus Normal?
Yes. About 1 in 3 adults experience tinnitus at some point in their lives. For most, it’s mild. But for 10–15%, it can be prolonged and bothersome, requiring medical help. Tinnitus is very real and should be addressed with care.
⚠️ What Causes Tinnitus?
- Hearing loss
- Loud noise exposure
- Ototoxic medications
- Head injuries
- Ménière’s disease
- High blood pressure
- Excessive earwax
- Certain tumors
🌙 Why Is Tinnitus Worse at Night?
At night, there are fewer background sounds to mask your tinnitus. As a result, it feels louder. Stress, anxiety, or fatigue can make it feel worse.
🩺 How Is Tinnitus Diagnosed?
Tinnitus is typically a symptom, not a condition. A hearing evaluation by an audiologist is recommended, along with a medical exam by an ENT to rule out other causes. Audiologic tests help determine the pitch, loudness, and impact of your tinnitus.
📈 Can Tinnitus Be Measured?
No. Tinnitus is subjective and cannot be directly measured. However, audiologists use your descriptions and hearing tests to understand its impact.
💡 Treatment Options
While there is no universal cure, several treatments can help reduce or manage tinnitus:
- Hearing Aids
- Tinnitus Sound Generators
- Relaxation Therapy
- Biofeedback & Counseling
- Habituation & CBT
- Sound machines or masking devices
- Electrical stimulation (in rare cases)
🎧 Do Hearing Aids Help with Tinnitus?
Yes. If you have hearing loss, hearing aids can:
- Amplify environmental sounds, reducing your awareness of tinnitus
- Be combined with sound generators that produce soothing tones
- Help retrain your brain to focus less on tinnitus over time