Free Consultation
Definition of Hearing Loss
Hearing loss—also known as hearing impairment—is a partial or total inability to hear. It occurs when sound signals are not effectively processed by the ear or the brain. People with hearing loss may find that some sounds are too soft, muffled, or even completely missing, especially in noisy environments.
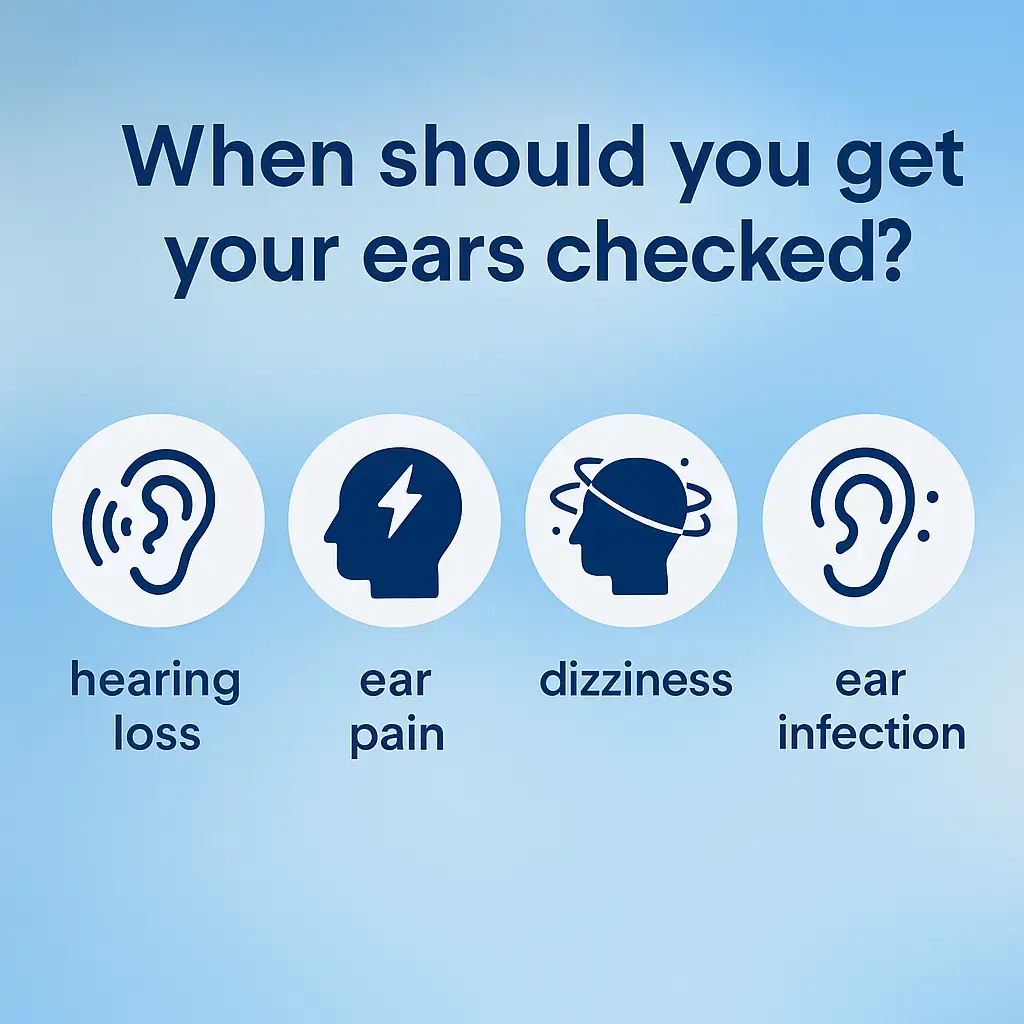
When Should You Get Your Ears Checked?
-
If you’re experiencing any of the following symptoms, it’s time to schedule a hearing test:
- Pain, discharge, or ringing in the ears (tinnitus)
- Sudden imbalance or vertigo
- Difficulty understanding speech, especially in noisy environments
- Needing to speak louder to catch someone’s attention
- Struggling to hear soft sounds like rustling leaves or whispering
- Perception that high-pitched sounds are too loud or distorted
- Hearing clearly in one ear but not the other (unilateral hearing loss)
Remember: Hearing loss is often progressive. Timely intervention can prevent further deterioration.
Degrees of Hearing Loss
| Degree | Description |
|---|---|
| Mild | Trouble hearing soft sounds like whispers or rustling leaves |
| Moderate | Difficulty following conversations at normal speaking volume |
| Severe | Only able to hear loud voices or shouting |
| Profound | May not hear even very loud sounds |
Types of Hearing Loss
- Conductive Hearing Loss
- Sensorineural Hearing Loss
- Mixture of Conductive & Sensorineural Hearing Loss
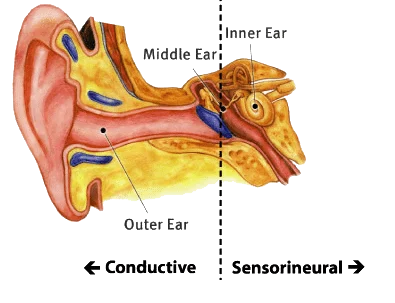
Conductive Hearing Loss
Caused by obstructions or damage in the outer or middle ear.
Common Causes:
- Wax buildup
- Ear infections (glue ear)
- Perforated eardrum
- Eustachian tube dysfunction
- Ossicular bone abnormalities
Treatment: Can often be corrected through medicine or surgery, but if not, hearing aids are highly effective.
Sensorineural Hearing Loss
Often called "nerve deafness", this involves damage to the inner ear (cochlea) or auditory nerve.
Common Causes:
- Ageing (presbycusis)
- Prolonged exposure to loud noise
- Hypertension
- Ototoxic medications
- Genetic or congenital factors
- Neurological disorders
Treatment: This type of hearing loss is usually permanent, and hearing aids offer the best solution.
Mixed Hearing Loss
A combination of conductive and sensorineural hearing loss, involving both the outer/middle ear and inner ear or nerve pathways.
Treatment: May involve a combination of medical, surgical, and hearing aid solutions, depending on the severity and underlying cause.
What is Tinnitus?
Tinnitus refers to hearing sounds—like ringing, buzzing, or hissing—in the absence of external noise. It’s a subjective condition often associated with hearing loss.
Common Causes:
- Ear infections
- Wax buildup
- Otosclerosis
- High blood pressure
- Excessive smoking or alcohol use
- Certain medications
- Neurological disorders
Management
Management: While there’s no universal cure, hearing aids with tinnitus masking features can offer significant relief in many cases.
At Denoc, we understand how deeply hearing loss can impact daily life. Whether you suspect mild hearing difficulty or have been living with long-term hearing challenges, early detection and the right solution can make all the difference. We offer comprehensive diagnostics and a wide range of advanced hearing aids tailored to your needs.

Book a Hearing Test Today:
Your hearing health matters. Don’t delay—reach out to our experts at Denoc Hearing in Chennai, Bangalore, or any of our centres across India.
Frequently asked questions
If you frequently ask others to repeat themselves, struggle to hear in noisy environments, or feel like people are mumbling, you may have hearing loss. Other signs include ringing in the ears (tinnitus), imbalance, and needing to increase the volume on devices. A professional hearing test is the best way to know for sure.
There are three main types of hearing loss:
- Conductive Hearing Loss – caused by issues in the outer or middle ear (e.g., wax buildup, infections).
- Sensorineural Hearing Loss – caused by damage to the inner ear or auditory nerve, often permanent.
- Mixed Hearing Loss – a combination of both types, involving multiple parts of the hearing pathway.
Some types, like conductive hearing loss, may be treated medically or surgically. Sensorineural hearing loss is usually permanent, but hearing aids offer effective management. For mixed hearing loss, treatment may include both medical intervention and hearing aids.

