Middle Ear Analysis for Accurate Diagnosis
What is Impedance Audiometry?
Impedance audiometry is a non-invasive diagnostic test used to evaluate the functioning of the middle ear, particularly the tympanic membrane (eardrum) and the ossicular chain. This test involves tympanometry and acoustic reflex measurements, which provide essential information about the middle ear system without directly measuring hearing sensitivity.
It also helps assess the acoustic reflex pathways involving the facial (CN VII) and auditory (CN VIII) cranial nerves and the brainstem, playing a vital role in the differential diagnosis of auditory disorders.
Purpose of the Test
- To check the mobility and pressure of the eardrum
- To detect middle ear pathologies like fluid build-up, eustachian tube dysfunction, or perforation
- To evaluate acoustic reflexes, aiding in neurological assessments
- To complement pure tone audiometry in diagnosing hearing loss
Note: This test alone does not determine hearing thresholds but is interpreted alongside other audiological tests.
Online simple step for appointment
Clinical Procedure
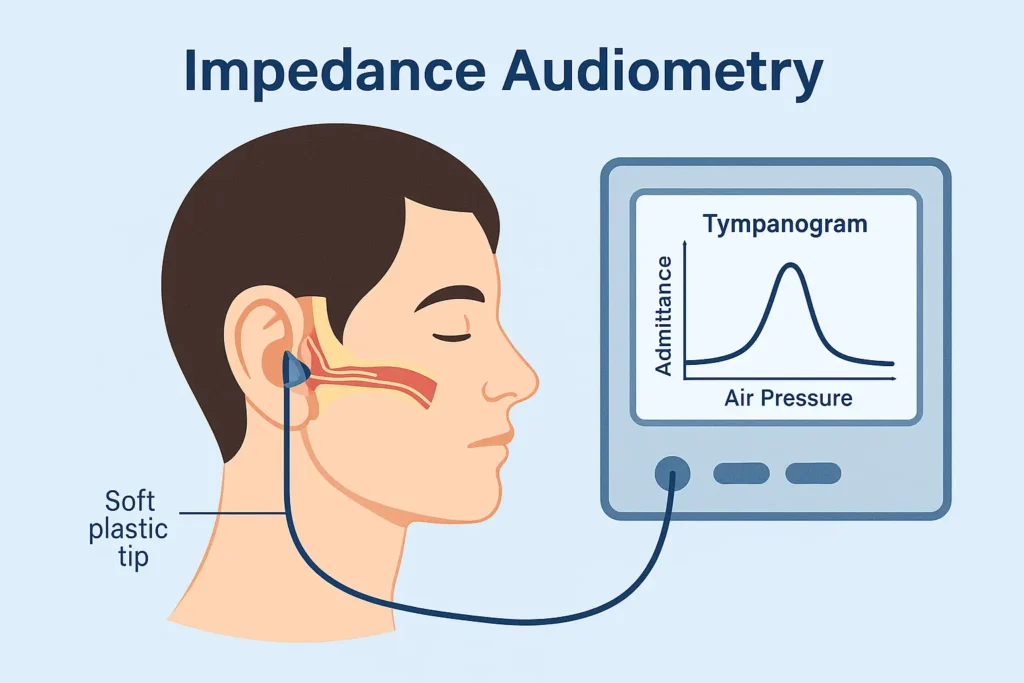
- A soft plastic probe is gently placed in the ear canal to create an airtight sea
- A probe tone (typically 226 Hz) is introduced while air pressure in the canal is varied from +200 daPa to -400 daPa.
- The equipment measures admittance (ease of sound flow) and produces a tympanogram—a graphical representation of middle ear function.
Patient Preparation
Test Duration
- Average Time: 15 – 20 minutes
- Report Delivery: Results and interpretation will be provided immediately after the test.
Why Choose Denoc Hearing for Impedance Audiometry?
- Advanced diagnostic equipment
- Audiologists trained in middle ear diagnostics
- Immediate report and follow-up consultation
- Conveniently located in Chennai with expert care
Frequently asked questions
No, the test is completely safe and painless. You may feel mild pressure in the ear during the procedure.
While it doesn’t measure hearing thresholds directly, it helps detect middle ear abnormalities that may affect hearing.
Yes, but for infants under 7 months, specialized high-frequency tympanometry may be more appropriate.