Worried about early hearing loss or suspect issues in infants?
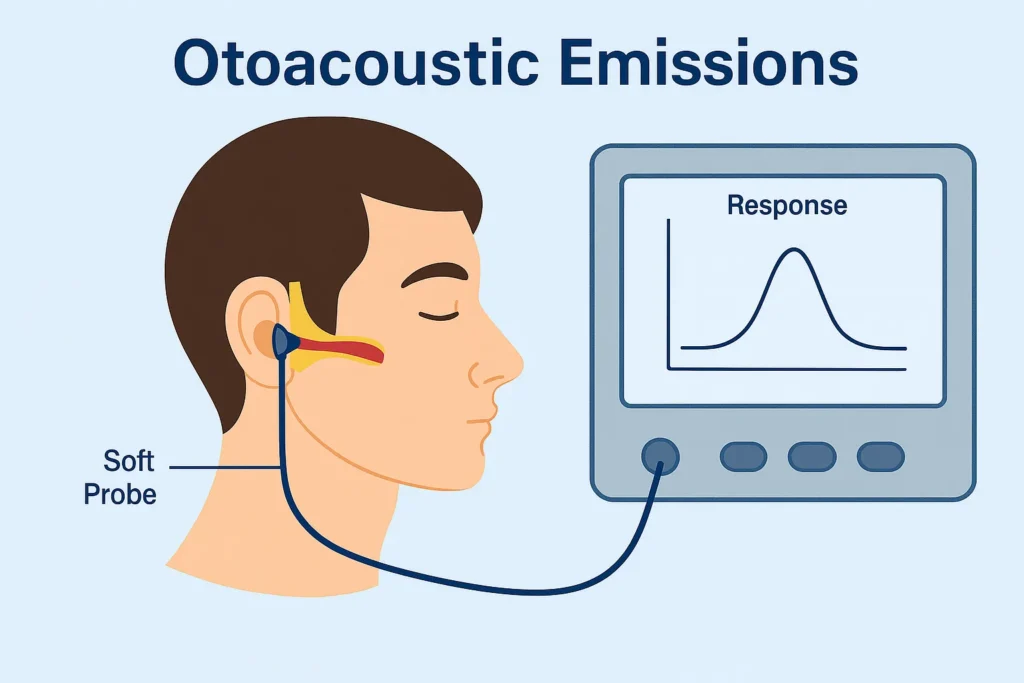
The Otoacoustic Emissions (OAE) test is a quick, non-invasive screening tool used to assess the function of the inner ear, specifically the outer hair cells in the cochlea.
What is an OAE Test?
Otoacoustic Emissions (OAE) are low-level sounds generated by the outer hair cells of a healthy cochlea in response to auditory stimulation. These sounds are measured to determine whether the inner ear (specifically the cochlea) is working properly.

The presence or absence of these emissions helps audiologists at Denoc Hearing identify:
- Early-stage sensorineural hearing loss
- Cochlear (inner ear) dysfunction
- Hearing loss in infants, newborns, or non-cooperative adults
- Auditory neuropathy in further evaluation
How is the OAE Test Performed?
The test is quick, completely painless, and often performed during newborn hearing screening, or as a preliminary test in hearing loss evaluation.
Types of OAE Tests

Transient Evoked OAE (TEOAE) – brief clicks used; ideal for newborn screening

Distortion Product OAE (DPOAE) – two tones at different frequencies played simultaneously; used in adults and older children
Patient Preparation
Test Duration
The OAE test typically takes 5 to 15 minutes per ear, and results are available immediately.
Why Choose Denoc for ABR Testing?
- Ideal setup for infant and pediatric hearing screening
- Experienced audiologists and child-friendly atmosphere
- Accurate and reliable cochlear health insights
- Used as part of newborn hearing screening protocol
Frequently asked questions
OAE testing is recommended for newborns, infants, and individuals who cannot respond behaviorally to traditional hearing tests. It’s also useful in early detection of cochlear hearing loss.
A normal OAE result suggests normal outer hair cell function, but further tests (like PTA or BERA) may be needed to assess neural pathways and complete hearing evaluation.
Yes. OAE testing can be useful in adults to monitor cochlear function, especially in ototoxicity, noise-induced hearing loss, or monitoring auditory neuropathy.