Universal Newborn Hearing Screening (UNHS) is indeed a vital public health initiative aimed at early detection of hearing loss in newborns. Here are some key points highlighting the importance of UNHS:
Early Diagnosis and Intervention: UNHS allows for the early identification of hearing loss in infants. Early diagnosis is crucial because it provides an opportunity for timely intervention and support.
Cognitive Development: Hearing is integral to a child’s cognitive development. Children learn to communicate, develop language skills, and acquire knowledge through auditory experiences. Detecting and addressing hearing loss early can significantly impact a child’s cognitive development.
Preventing Speech and Language Delays: When hearing loss goes undiagnosed in infants, it can lead to speech and language delays. UNHS helps in preventing these delays, ensuring that children can develop age-appropriate communication skills.
Communication and Social Skills: Hearing loss can affect a child’s ability to communicate effectively and interact socially. Early intervention through UNHS can mitigate these challenges and enhance a child’s ability to engage with their family and peers.
Academic Success: Children with hearing loss may encounter academic difficulties if their condition is not identified and managed early. UNHS can contribute to better academic outcomes by addressing hearing loss promptly.
Quality of Life: Early detection and intervention can lead to an improved quality of life for children with hearing loss. It allows them to access the necessary support, including hearing aids or cochlear implants, and develop essential communication skills.
Regarding the testing process:
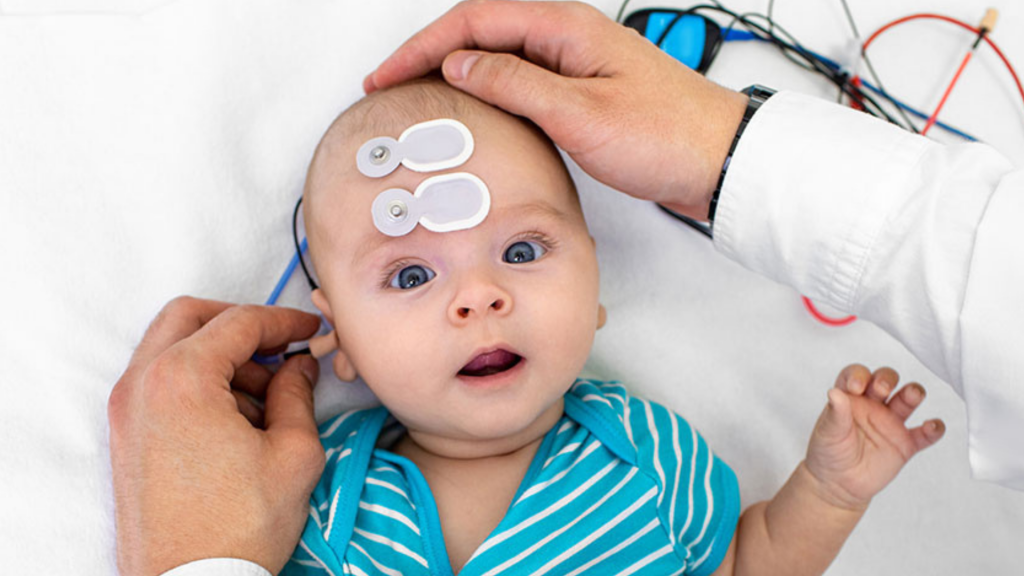
Newborn Hearing Screening: This is typically performed by an audiologist in a hospital setting shortly after birth. It is a safe, simple, and painless procedure that takes only a few minutes.
Referral for Further Testing: If a newborn fails the initial screening, they are referred to a pediatric audiologist for more comprehensive testing to confirm the hearing loss.
Diagnostic Auditory Brainstem Response (ABR) Test: If the second round of testing confirms hearing loss, a diagnostic ABR test is conducted. This test provides more detailed information about the nature and degree of hearing loss.
Early Intervention: If hearing loss is diagnosed, it is essential that appropriate services and interventions begin as soon as possible, preferably no later than six months of age. A team of professionals, including audiologists, speech therapists, and early intervention specialists, may work with the child and their family to provide the necessary support and services.
Early detection through UNHS and timely intervention can significantly improve the long-term outcomes for children with hearing loss, ensuring that they have the best possible opportunities for development and a fulfilling life.
0 comment